Salts and esters of propionic acid and anions CH3CH2CO2− are known as propionates or propanoates. It is a colourless oily liquid with a rancid smell that produces irritating vapour. Propionic acid is a short-chain saturated fatty acid that consists of ethane attached to the carbon of a carboxy group. Let us know the chemical properties of propionic acid.
Chemical Properties Of Propionic Acid
| Chemical formula | C3H6O2 or CH3CH2COOH |
| Molecular weight | 74.079 g/mol |
| Density | 0.98797 g/cm3 |
| Chemical names | Propanoic Acid
Ethanecarboxylic acid |
| Boiling point | 141.15 °C |
| Melting point | −20.5 °C |
| Crystal structure | Monoclinic |
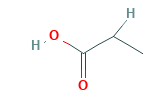
Propionic Acid Structural Formula
The structural representation of Propionic Acid is as shown in the figure below. It is used in the production of chemicals and polymers.
Uses Of Propionic Acid
- Propionic acids are used in industrial applications.
- Propionic acids are used in biological applications.
To learn more about various scientific figures and facts stay tuned with BYJU’S!!
Comments